The “blue ocean strategy,” proposed by W. Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne in the book Blue Ocean Strategy (2005), focuses on developing new markets to make competition irrelevant. Instead of competing in saturated markets, which the authors call “red oceans,” companies should innovate to create uncontested market spaces, called “blue oceans.”
The blue ocean strategy is based on two main pillars: value innovation and the reconstruction of market boundaries. Value innovation consists of simultaneously offering high added value to customers and reducing costs, challenging the traditional dichotomy of “more value costs more.” Reconstructing market boundaries involves identifying and capturing opportunities in adjacent sectors that are not yet exploited, avoiding direct competition and generating new demand.
The extended edition of the book added the idea of alignment.
According to Kim and Mauborgne, to implement the blue ocean strategy effectively, alignment between various elements of the company is crucial. This alignment occurs in the value proposition, profit proposition and people proposition (Figure 1).
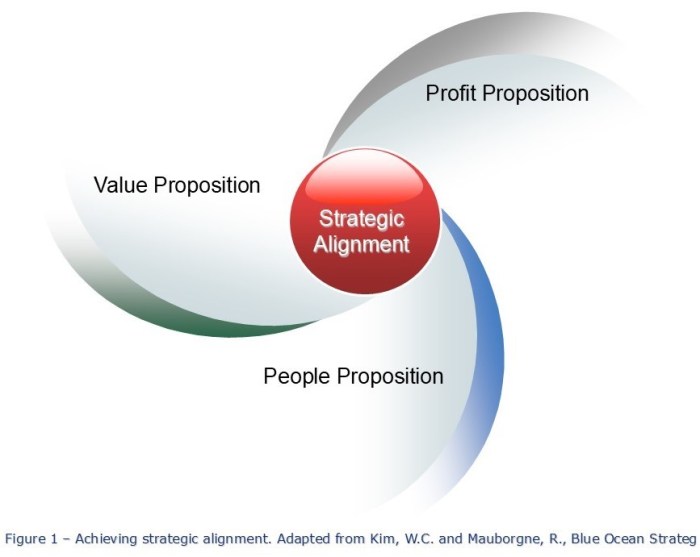
Aligning the value proposition involves offering products and services that attract new customer segments and generate new demand. It’s what buyers get from an offer minus the price they pay.
Example: Cirque du Soleil combined elements of circus and theater to create a new form of entertainment.
Aligning the profit proposition involves adjusting processes and operations to support value innovation, including simplification and cost reduction. It represents the revenue a company generates from an offering minus the cost to produce and deliver it.
Example: Companies adopt innovative technologies to increase efficiency and reduce waste.
Aligning the people proposition—the organizational, incentive and recognition system—ensures that the entire company is committed to the blue ocean vision and strategies, in order to reward and encourage behaviors that promote value innovation.
Examples: Training and clear communication to all employees about the new strategic direction and incentive programs for teams developing new products or services aligned with the blue ocean strategy.
Well-developed alignment provides:
- Strategic coherence: all parts of the company work synergistically, promoting a unified effort in creating a blue ocean.
- Efficiency and effectiveness reduces redundancy and optimizes resources, increasing the organization’s ability to innovate and respond quickly to changes.
- Engagement and motivation: employees aligned with the company’s vision tend to be more committed and motivated.
The Blue Ocean Strategy, when implemented with strong internal alignment, can result in sustainable competitive advantage, significant growth, and continuous innovation for the company.